
Ransomware has become one of the most devastating forms of cybercrime in the modern era. From hospitals forced to cancel surgeries to global supply chains brought to a standstill, ransomware doesn’t just lock data—it cripples organizations.
The damage goes far beyond financial losses. Ransomware can erode trust, tarnish reputations, and create lasting business disruption. With attackers now leveraging automation, double extortion, and ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS), no organization—large or small—is immune.
To combat this threat, enterprises and MSSPs must go beyond traditional antivirus and backups. Seceon’s AI/ML and Dynamic Threat Modeling (DTM)-powered ransomware detection solutions deliver real-time visibility, rapid detection, and automated containment—ensuring businesses stay resilient even under attack.
Ransomware is a type of malicious software that encrypts files, locks systems, or steals sensitive data, demanding payment (usually in cryptocurrency) in exchange for restoring access.
Key features of ransomware:
In short, ransomware transforms valuable data into leverage, turning cybercrime into a multi-billion-dollar extortion industry.
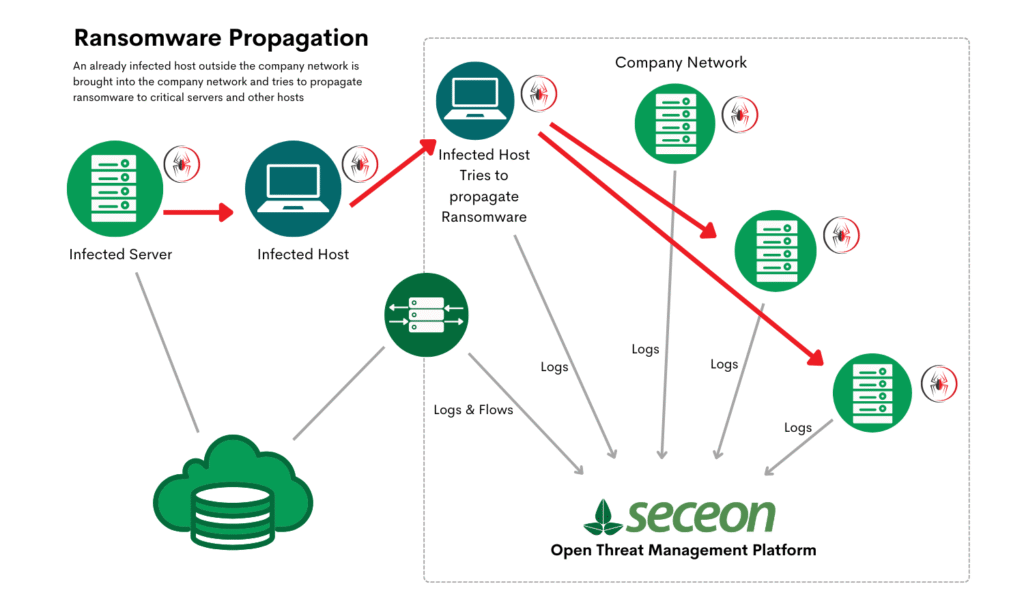
Ransomware typically follows a multi-stage attack lifecycle:
Sophisticated ransomware groups also disable backups, security software, and monitoring tools before triggering encryption, making recovery even harder.
Ransomware comes in many forms. The most common types include:
Several high-profile ransomware attacks highlight the devastating impact:
These examples underscore how ransomware has evolved from random infections to targeted, strategic cyber campaigns.
While any organization can fall victim, attackers typically target:
Attackers often select victims based on impact and ability to pay, prioritizing industries where downtime is catastrophic.
Cybersecurity experts and law enforcement generally advise not paying the ransom. Reasons include:
Instead, organizations should focus on proactive prevention, incident response, and recovery strategies that minimize damage without funding criminals.
Once ransomware strikes, removal and recovery must be carefully handled:
While removal may restore operations, the best approach is detecting and blocking ransomware before it activates.
Seceon Inc. provides a modern, AI/ML-powered defense against ransomware that goes beyond traditional tools. Our aiXDR-PMax, aiSIEM, and aiSecurityScore360 solutions are designed to deliver real-time ransomware detection, automated containment, and continuous protection.
Seceon’s patented Dynamic Threat Modeling (DTM) continuously learns user, device, and application behavior. Any anomalies—such as mass file encryption, unusual data exfiltration, or privilege escalation—are instantly flagged and stopped.
When ransomware-like behavior is detected, Seceon automatically:
With single-pane-of-glass monitoring, Seceon unifies logs, flows, and events across endpoints, networks, cloud, and applications. This ensures ransomware cannot hide in silos or blind spots.
Seceon’s aiSecurityScore360 continuously monitors for misconfigurations and vulnerabilities that ransomware exploits. Risk scores prioritize remediation before attacks occur.
For Managed Security Service Providers, Seceon enables multi-tenant ransomware defense—allowing MSSPs to protect hundreds of customers efficiently and cost-effectively.
Unlike legacy tools, Seceon delivers:
With Seceon, organizations can stay resilient against ransomware, avoid paying ransoms, and protect their reputation, data, and customers.
Q1: What is ransomware?
A: Ransomware is malicious software that encrypts files or locks systems, preventing access to data until a ransom (commonly cryptocurrency) is paid. Modern variants also exfiltrate data for double-extortion. Effective protection includes backups, endpoint detection, and network monitoring.
Q2: How do ransomware attacks typically work?
A: Ransomware attacks usually start with initial access (phishing, exposed RDP, vulnerabilities), then escalate privileges, move laterally, deploy the payload, encrypt data, and finally demand ransom. Attackers often disable backups and security tools before encrypting to maximize impact.
Q3: What are common indicators of a ransomware infection?
A: Signs include sudden high-volume file encryption, unusual file extensions, large outbound data transfers, unexpected process creation on endpoints, disabled security agents, and ransom notes appearing on multiple hosts.
Q4: Should organizations pay the ransom if infected?
A: Security experts and law enforcement generally advise against paying, as it encourages criminals and doesn’t guarantee data recovery. Instead, isolate systems, engage incident response, and restore from verified backups when possible.
Q5: How can organizations prevent ransomware?
A: Preventive measures include strong patch management, multi-factor authentication (MFA), least-privilege access, secure configuration, network segmentation, regular offline backups, employee phishing training, and AI-driven detection for early anomaly spotting.
Q6: What is the fastest way to stop ransomware spread once detected?
A: Immediately isolate infected endpoints and network segments, block malicious IPs/domains, revoke compromised credentials, and engage automated containment playbooks. The faster containment begins, the lower the overall damage.
Q7: How do backups help in ransomware recovery?
A: Verified, immutable, and offline backups enable organizations to restore encrypted data without paying ransom. Ensure backups are segregated from networks, tested regularly, and include versioning to recover clean copies.
Q8: What technical solutions detect ransomware early?
A: Modern detection uses AI/ML behavioral analytics, endpoint telemetry, network flow analysis, threat intelligence, dynamic threat modeling, and correlation across logs (SIEM/aiSIEM) and XDR solutions to spot unusual activity before encryption.
Q9: How does Seceon protect against ransomware?
A: Seceon uses AI/ML and Dynamic Threat Modeling (DTM) via aiSIEM and aiXDR-PMax to detect anomalies (mass file operations, privilege escalation, lateral movement), automate containment (isolate endpoints, block traffic), and provide continuous vulnerability and exposure scoring with aiSecurityScore360.
Q10: What should incident response include after a ransomware attack?
A: An effective response includes containment, forensic investigation to determine root cause, assessing data loss/exfiltration, restoring systems from clean backups, patching exploited vulnerabilities, credential resets, regulatory notification (if required), and post-incident hardening.
Q11: How can small businesses defend against ransomware affordably?
A: Small businesses should prioritize MFA, automated patching, secure backups, staff training, endpoint protection, and consider managed detection services (MSSPs) or cloud-native XDR solutions to get enterprise-level protection without large upfront costs.
Q12: How often should organizations test ransomware preparedness?
A: Run tabletop exercises, restore tests, and simulated phishing campaigns at least quarterly. Full disaster recovery and backup restores should be tested semi-annually or according to criticality.
Ransomware is not just a passing trend—it’s the defining cyber threat of our time. Organizations must prepare not just to react, but to proactively prevent, detect, and respond.
Seceon’s AI/ML-powered ransomware detection and response platform provides exactly that—comprehensive visibility, proactive defense, and automated resilience. Whether you are a large enterprise, a healthcare provider, or an MSSP protecting hundreds of clients, Seceon equips you with the tools to stop ransomware in its tracks.
Don’t wait for ransomware to strike—detect, prevent, and protect with Seceon.
